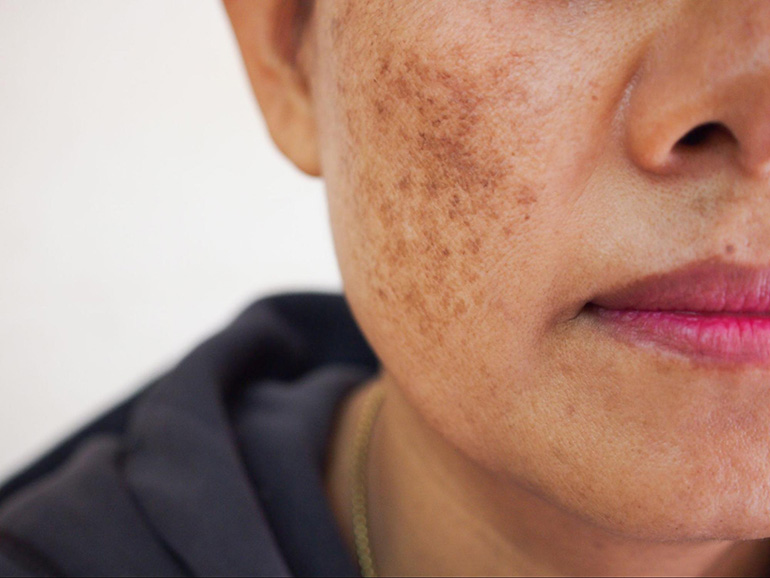
Melasma & Hyperpigmentation
There are several types of hyperpigmentation, each with its causes and characteristics:
- Melasma: This is a type of hyperpigmentation that is triggered by sun exposure as well as hormonal changes, such as pregnancy, the use of birth control pills, or menopause, or It appears as dark, patchy areas on the face, neck, and forearms.
- Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH): This type of hyperpigmentation occurs as a result of skin inflammation or injuries, such as acne, eczema, psoriasis, or a wound. It appears as dark spots or patches that are often uneven in texture.
- Freckles: also known as ephelides, these are small, flat, brown spots that are often inherited and appear on the areas that are exposed to the sun.
- Sunspots: also known as age spots, these are flat, brown spots that develop on the skin after years of sun exposure. They most commonly appear on the face, hands, and other body areas frequently exposed to the sun.
- Hyperpigmentation from medication: Some medications, such as certain antibiotics, chemotherapy drugs, and anti-seizure medications, can cause hyperpigmentation as a side effect.
Most of these dark spots or patches are of cosmetic concern, but they can be a medical problem. Therefore, identifying the type of hyperpigmentation that can help determine the underlying cause and the most effective treatment options is important.
Melasma is a type of hyperpigmentation that causes dark, patchy areas to appear on the skin, usually on the face, neck, and forearms. It is a common condition that occurs more often in women and is often triggered by hormonal changes, such as pregnancy, menopause, or birth control pills.
Melasma is caused by an overproduction of melanin, the pigment that gives colour to our skin and can be worsened by exposure to sunlight. While melasma is not a serious medical condition, it can burden some people, as the dark patches can be difficult to conceal and treat.
Treatment for melasma may involve topical creams or gels containing ingredients like hydroquinone, retinoids, or azelaic acid, which lighten the skin. In some cases, chemical peels, microdermabrasion, or laser therapy may also be recommended. It is essential to avoid sun exposure and wear sunscreen daily to help prevent the development or worsening of melasma.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are the Factors That Can Trigger Hyperpigmentation?
There are several factors that can trigger hyperpigmentation, including:
- Sun Exposure: Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun stimulates melanocytes to produce more melanin in order to protect the skin from damage.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal changes during pregnancy, menopause, and taking birth control pills can trigger the overproduction of melanin, leading to a condition called melasma.
- Inflammation: Skin inflammation caused by conditions such as acne, eczema, and psoriasis can trigger melanocytes to produce more melanin.
- Injury: Injuries to the skin, such as cuts, burns, and insect bites, can also cause hyperpigmentation as part of the healing process.
- Genetic Factors: Some people may be more prone to hyperpigmentation due to genetic factors.
Overall, hyperpigmentation occurs when there is an imbalance in melanin production, leading to an accumulation of melanin in certain areas of the skin.
What Are the Risks of Developing Melasma?
The exact cause of melasma is not well understood. However, there are some risk factors involved in developing melasma, including:
- Hormonal changes: Melasma is often triggered by hormonal changes, such as while taking birth control pills, during pregnancy, menopause, or being on hormone replacement therapy.
- Sun exposure: Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun can trigger melasma or make it worse. This is because UV radiation stimulates the production of melanin in the skin, which can lead to the development of dark patches.
- Genetics: Genetics play roles in developing melasma in some people predisposed to developing melasma than others.
- Ethnicity: Melasma is more common in people with darker skin tones, such as Hispanic, Asian, or African descent.
- Cosmetics and skincare products: Certain cosmetics and skincare products can irritate the skin and trigger melasma in some people.
While melasma is not a serious medical condition, it can be a cosmetic concern for some people. The best prevention is to avoid known triggers, such as sun exposure, and to use sunscreen daily. If you are pregnant or taking hormonal medications, talk to your healthcare provider about ways to reduce your risk of developing melasma.
How is Melasma Treated?
The most common treatment for melasma involves a combination of topical medications, sunscreen, and lifestyle changes.
Here are some of the treatments used for melasma:
- Topical medications: Hydroquinone is the most commonly used medication for melasma treatment. It is a skin-lightening agent that inhibits melanin production. Other commonly used medications include tretinoin, azelaic acid, and kojic acid.
- Sun protection: Sunscreen is a crucial part of melasma treatment, as exposure to the sun can worsen the condition. Patients are advised to use broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 50 or over and to wear protective clothing such as hats and sunglasses.
- Chemical peels involve applying chemicals which exfoliate the outer layers and remove the dark spots. This treatment is usually done by a dermatologist and can help improve melasma’s appearance.
- Laser therapy: using a high-energy laser to remove the dark spots. This treatment can be effective for some patients, but it is not suitable for everyone.
- Lifestyle changes: Certain lifestyle changes can help to improve melasma, such as avoiding exposure to the sun and wearing protective clothing, avoiding hormonal medications or contraceptives, quitting smoking, and managing stress.
It is important to note that melasma can be a complex condition to treat, and it may take several months of consistent treatment before significant improvement is seen.
Dr Miller is here to help
Are you suffering from stubborn dark spots or patches? You are not alone!
Dr Miller has been on a melasma & hyperpigmentation journey herself as well as helping many people who suffer from these conditions. Hence it is her passion to help you get better.
At the consultation, Dr Miller will review your medical history to understand any underlying medical conditions or medications contributing to your melasma/hyperpigmentation. She will also ask about your skincare routine, including the products you use and any recent changes you have made.
Then she will examine the affected area and evaluate the severity of your melasma. She may use a special device called a Wood’s lamp to help them see the pigmentation more clearly.
Based on your medical history and physical examination, Dr Miller will recommend a personalised treatment plan that may include topical and oral medications, sunscreen, lifestyle changes, and/or other treatments such as chemical peels or laser therapy. She will explain each treatment option’s benefits and potential side effects and help you decide which treatments are right for you.
Depending on the severity of your melasma and the treatment plan recommended, you may need to schedule follow-up appointments with Dr Miller to monitor your progress and adjust your treatment plan as needed.